Degenerative osteoarthritis of the joints, as the progression of which leads to the destruction of cartilage tissue, is often diagnosed in men and women at a young age. The characteristic symptoms of an incipient disease are severe pain, which also occurs at rest, if the limbs are not put under pressure. To relieve unpleasant discomfort and prevent the destruction of cartilaginous structures, complex treatment is prescribed.
What is this disease?
Osteoarthritis is a terrible, common chronic condition that affects most of the entire population.
The pathology is characterized by inflammatory lesions of the cartilage tissue of small and large joints. Due to degenerative changes in the cartilage, the periarticular capsule, the synovial membrane, the muscle and ligament structures as well as the bone tissue are affected. The main cause of the development of such a pathology is considered to be impaired metabolism. Complete cure of the disease is impossible, it will only be possible to bring the patient into remission, which is why osteoarthritis, which gradually destroys the joint system, is dangerous. Joint diseases are often diagnosed in old age, but also occur in young people who are over 20 years old. It is important to diagnose the initial stages of its development. This will prevent new complications and help the body deal with the problem.
Reasons for development

The violation of metabolic processes in the articular joints triggers the onset of the development of the disease. The pathology is characteristic of one or more joints at the same time. Other common causes of osteoarthritis are:
- hormonal changes in menopausal women;
- Violation of the blood supply to the joints;
- constant hypothermia;
- chronic damage;
- advanced age;
- Obesity;
- increased stress on the joints;
- Autoimmune pathologies;
- diseased thyroid;
- Hemophilia;
- Herpes;
- Hepatitis;
- Allergies that affect bone and joint structures;
- Varicose veins;
- strict diets or unbalanced meals;
- excessive physical activity;
- Inheritance;
- unfavorable environment.
Arthritic changes are observed in people who have to work in difficult physical conditions. These are such specific specialties:
- Miners;
- Bricklayer;
- Metallurgists;
- Wrought;
- Angler.
Stages and characteristic symptoms
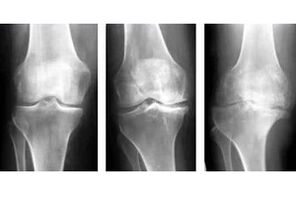
Signs of osteoarthritis develop gradually and increase as the pathology progresses. There are 3 stages of osteoarthritis:
- In the first stage, there is no morphological change, only the synovial composition of the fluid is disturbed, as a result of which the cartilage tissue receives less nutrients, quickly loses its elasticity and stamina. There is inflammation in the joint cavity, pain starts to bother.
- In stage II, the degenerative process develops more actively. The cartilage of the joints is gradually destroyed, uric acid is not completely eliminated from the body, as a result of which the first bone growth occurs in the joint. This restricts movement of the joint so that the inflammation progresses and interferes with persistent pain in the muscles of the extremities.
- Grade III is manifested by complete thinning of the cartilage tissue of the joint, and deformation of the joint itself is also observed. There are signs of axial changes in the limb. Degenerative disorders in the ligamentous apparatus also begin, as a result of which the limb can no longer move normally, hypermobility in combination with a violation of the natural range of motion is observed. The pain in stage 3 osteoarthritis is constant, a person can not lie still, sleep, rest. Complete malnutrition of the joint threatens to disrupt the function of the affected extremity.
Other symptoms

The disease causes characteristic signs in a person, which are conventionally divided into 4 groups:
- Pain. Severe joint pain that does not go away for a long time is the first symptom that marks the progression of the pathology. Pain is caused by any movement or physical activity, but at rest the person gets better and the discomfort subsides.
- Crunch. This symptom manifests itself in the stage of exacerbation of osteoarthritis. Due to the fact that the cartilage tissue of the joints is deformed over a long period of time, the bone structures begin to touch and rub against each other. As the crisis increases, so will the pain syndrome.
- Impaired joint mobility. Progressive osteoarthritis leads to an increased growth of the bone formations. As a result, the muscle tissue spasms, and the gap in the joint gradually decreases. The pressure in the joint increases, which also immobilizes the extremity.
- Joint deformity. The rapid growth of osteophytes can provoke a modification of the connection, but this symptom already develops in the later stages.
Types of osteoarthritis of the joints
Differentiate between idiopathic or primary osteoarthritis and secondary. The first type is an independent disease that occurs due to physiological, age-related changes. However, the secondary form arises against the background of chronic injuries and can manifest itself at any age - at the age of 20 or 30. Taking into account which joint is affected, a distinction is made between osteoarthritis:
- Shoulder or elbow joint;
- Hip or knee joint;
- Spine.
The disease also happens:
- refined;
- not specified.
Why is it dangerous?

Acute osteoarthritis is terrible because, in the course of the pathology, the spine is involved in degenerative processes, due to which hernias appear. Therefore, it is important to treat osteoarthritis effectively in the early stages of development, when conservative methods can be used. If the drugs are given late or the patient tries to heal himself, the following disorders will occur:
- Deformation and destruction of joint elements;
- Restriction of limb mobility;
- Disability;
- Violation of the biomechanics of the spine due to the fact that the intervertebral disc has subsided.
diagnosis
Before prescribing any effective treatment for osteoarthritis or removing the affected areas, it is important to know the exact diagnosis. Therefore, after the initial examination, the patient is sent to pass:
- general clinical analysis of blood and urine;
- Puncture of the synovial fluid if synovitis of the knee joint is suspected;
- a specimen for a histological examination of a biopath.
Instrumental diagnostics is carried out - radiography. If a patient has osteoarthritis of the knee (especially severe with varicose veins), x-rays of the knee joint should be taken. In the case of dysplasia and osteoarthritis of the hip joint, this area of the musculoskeletal system is examined. To determine the nature of the damage to cartilaginous structures, it is recommended to conduct an ultrasound, MRI or CT scan.
How do you treat?
Medically and surgically
Early osteoarthritis is treated with conservative therapy. The drugs are selected by a doctor strictly according to an individual scheme. If a person has a gastric ulcer or other pathologies of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, oral administration is contraindicated. In this case, injections will give the right effect. Correct prescription of drugs helps improve the activity of metabolic processes in the affected areas. Effective groups of drugs, thanks to which remission is prolonged:
- Anti-inflammatory;
- Hormonal corticosteroids;
- Chondroprotectors.
If conservative methods have not given results, surgical treatment is prescribed. Palliative operations are indicated to relieve the joint. If the joint is completely destroyed, surgical therapy is done to replace it. This is known as endoprosthetics. As new technologies have advanced in the field of prosthetics, people with a replaced joint can lead a different but fulfilling life.
Exercise therapy, physiotherapy, massage
Kinesitherapy is the name of a form of therapy that was developed by a renowned doctor. This is a series of physical exercises that must be done using special simulators. Regular exercise will help normalize the condition of the joint and improve its functionality. This means that it is recommended that the exercises be performed in special hospitals that specialize in musculoskeletal disorders.
Massage procedures performed by a chiropractor help normalize blood supply and nutrition in diseased areas, which gradually improves the condition of the joint joints. If the causes of osteoarthritis are clearly identified and there are no contraindications, then a number of physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed, for example, the following:
- Electrophoresis;
- Magnetotherapy;
- Laser treatment;
- Mud therapy;
- medical applications based on natural resins.
The need to diet
If osteoarthritis is caused by obesity, the patient is recommended to follow a diet that will help normalize body weight, which will significantly reduce the stress on the joints and improve their function. In order for the cartilage tissue to recover faster, doctors recommend that their patients eat jellies and broths cooked on bones more often. Thanks to the collagen contained in these shells, the connective tissue begins to regenerate and repair itself more quickly. It is also important to monitor the balance and completeness of the diet. The food should be varied and rich in vitamins, micro and macro elements.
prophylaxis
In order to avoid the progression of such a dangerous and serious disease, it is important to dose the load on the joints, especially the joints of the lower extremities. It is also worth avoiding injuries and fractures, after which the risk of osteoarthritis increases tenfold. It is important to lead an active lifestyle, exercise regularly in the morning, eat right, and monitor your weight. Thanks to these rules, it is possible to protect yourself from the appearance of destructive pathology or relapse.

























